- Leren door doen
- Trainers met praktijkervaring
- Klassikale trainingen
- Gedetailleerd cursusmateriaal
- Duidelijke inhoudsbeschrijving
- Maatwerk inhoud mogelijk
- Trainingen die doorgaan
- Kleine groepen
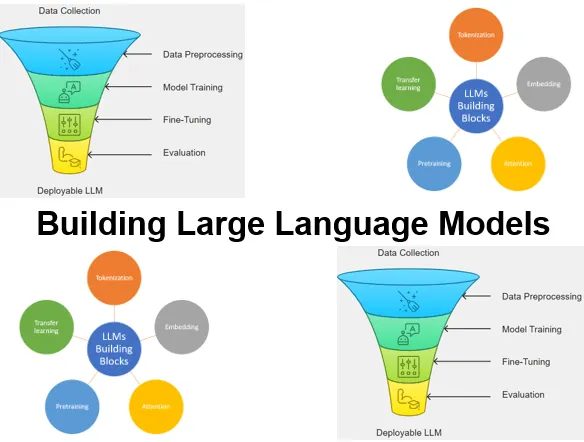
De cursus Large Language Models Bouwen van SpiralTrain leert je hoe je met PyTorch en modern tooling transformer-based LLMs ontwerpt, traint, fine-tuned en deployed. Je leert robuuste text pipelines en tokenizers op te zetten, een GPT-style model met pretraining te implementeren, instruction tuning en RAG toe te passen, en modellen in production op te leveren.
De cursus Large Language Models bouwen start met wat LLM’s zijn, waar ze worden ingezet en gaat in op de lifecycle van bouwen versus gebruiken. De Transformer/GPT-architectuur wordt geintroduceerd evenals hoe modellen leren van grote datasets en wanneer je klassieke QA gebruikt versus RAG.
Je leert ruwe tekst om te zetten naar modelklare tensors dor middel van tokenization token→ID mapping, speciale/contexttokens en sliding-window sampling. Embeddings en positional encodings worden behandeld en hoe om te gaan om met onbekende woorden.
Deze module demystificeert self-attention voor long-sequence modeling: queries, keys, values en causal masking om toekomstige tokens te verbergen. Positional encoding en multi-head attention worden toegvoegd toe om afhankelijkheden in input op te vangen.
Deze module behandelt PyTorch-basics—tensors en training loops evenals tooling om model kwaliteit te meten. Ingegaan wordt op feature scaling/normalization, activatie- en loss-functies en backpropagation.
Vervolgens bouw je MLP’s en CNN’s in PyTorch, kies je passende activaties en losses en implementeer je backpropagation. Ook NLP-specifieke preprocessing wordt behandeld evenals end-to-end binaire en multiclass-classificatie.
Daarna implementeer je een minimale GPT met layer normalization, residual connections en attention + feed-forward (GELU).
Je pretraint de LLM op ongelabelde tekst met next-token prediction en volgt training- versus validation-losses. Je verkent decoding strategies (bijv. temperature, top-k), beheerst randomness voor reproduceerbaarheid en slaat PyTorch-weights op/laadt ze in.
We bereiden datasets en dataloaders voor, initialiseren vanuit pretrained weights en voegen een classification head met softmax toe. Je traint en evalueert met loss/accuracy, met als voorbeeld een LLM-based spam-classification.
Tot slot oefen je supervised instruction tuning: datasets formatteren, efficiënt batchen en een pretrained LLM fine-tunen. Je evalueert outputs, exporteert responses/checkpoints en past parameter-efficiënte methoden zoals LoRA toe.
De cursus Large Language Models Bouwen is bedoeld voor engineers die transformer-based LLM’s willen ontwerpen.
Deelnemers dienen vertrouwd te zijn met Python. Ervaring met PyTorch of een vergelijkbaar Deep Learning-framework is een plus.
De training combineert bondige theorie met begeleide, hands-on labs. Via code-alongs bouw je een mini-GPT, bereid je datasets voor, voer je pretraining en fine-tuning uit en deploy je modellen.
Na afloop ontvangen deelnemers een certificaat van deelname aan de cursus Large Language Models Bouwen.
Module 1 : LLM Intro |
Module 2 : Working with Text Data |
Module 3 : Attentions Mechanism |
|
What is an LLM? Applications of LLMs Stages of Building LLMs Stages of Using LLMs Transformer Architecture Utilizing Large Datasets GPT Architecture Internals Learn Language Patterns Retrieval Augmented Generation Question and Answer Systems QA versus RAG Building an LLM |
Word Embeddings Decoders and Encoders Decoder Only Transformer Tokenizing text Convert Tokens into IDs Special Context Tokens Understand Sentence Structure Byte Pair Encoding Unknown Words Sampling with Sliding Window Creating Token Embeddings Encoding Word Positions |
Modeling Long Sequences Capturing Data Dependencies Attention Mechanisms Attending Different Input Parts Using Self-Attention Trainable Weights Hiding Future Words Positional Encoding Causal Attention Masking Weights with Dropout Multihead Attention Stacking Attentions Layers |
Module 4 : Pytorch Deep Learning |
Module 5 : Neural Networks |
Module 6 : GPT from scratch |
|
Deep Learning Intro Overview of PyTorch PyTorch Tensors Tensor Operations Model Evaluation Metrics Feature Scaling Feature Normalization Categorical Features Activation Functions Loss Functions Backpropagation |
Neural Networks Intro Building NN with PyTorch Multiple Layers of Arrays Convolutional Neural Networks Activation Functions Loss Functions Backpropagation Natural Language Processing Stopword Removal Binary Classification Multi-class Classification |
Coding an LLM Architecture Layer Normalization Normalizing Activations Feed Forward Network GELU Activations Adding Shortcut Connections Connecting Attention Weight Tying Linear Layers in Transformer Block Coding the GPT Model Generating Text |
Module 7 : Pretraining |
Module 8 : Tuning for Classification |
Module 9 : Fine-Tuning |
|
Pretraining on Unlabeled Data Calculating Text Generation Loss Training Losses Validation Set Losses Training an LLM Decoding Strategies Control Randomness Temperature Scaling Saving Model Weights in PyTorch Loading Pretrained Weights |
Categories of Fine-Tuning Preparing the Dataset Creating Data Loaders Top-k Sampling Soft-Max Function Initializing with Pretrained Weights Adding Classification Head Classification Loss and Accuracy Fine-tuning on Supervised Data Using LLM as Spam Classifier |
Instruction Fine-tuning Supervised Instruction Preparing a Dataset Organizing Training Batches Creating Data Loaders Loading a pretrained LLM Fine-tuning the LLM Extracting and Saving Responses Evaluating Fine-tuned LLM Fine Tuning with LoRA |
