-
Learning by doing
-
Trainers with practical experience
-
Classroom training
-
Detailed course material
-
Clear content description
-
Tailormade content possible
-
Training that proceeds
-
Small groups
The course NoSQL Data Access from SpiralTrain deals with various forms of NoSQL databases, where the data is stored differently than in traditional relational databases.
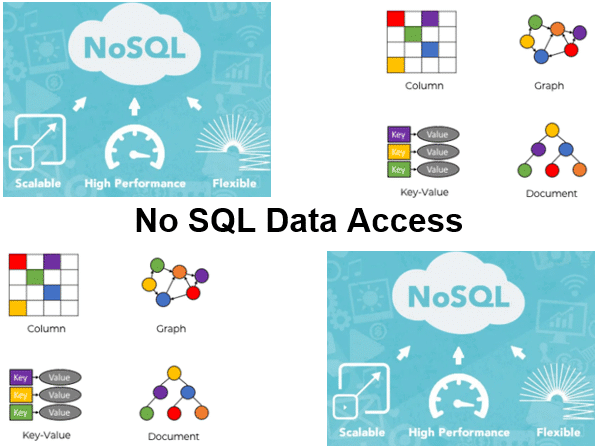
NoSQL databases are not table oriented and are mainly used to increase the speed of data access and the scalability for large numbers of users. The main types of NoSQL databases are discussed in the course such as wide-columns stores, key-values stores, document databases and graph databases.
Attention is paid to data storage in Google Big table as an example of a column oriented store. This also includes distributed storage and column families, versioning and null handling.
The operation of Cassandra and Redis as implementations of key-value stores is discussed as well. The use of associative arrays and data storage in the cache is explained.
Document oriented databases such as MongoDB and CoucheDB are also discussed. The various document formats such as JSON, XML and YAML and their applications are the subject of the course program.
Finally attention is paid to GrapQL databases of which Neo4J is a well-known example. This includes a discussion of Cypher Queries and Path Finding Queries.
The course NoSQL Data Access is intended for developers and other interested parties who want to get to know the possibilities and applications of NoSQL databases.
Knowledge and experience with SQL and approaching relational databases is beneficial for understanding, but not strictly necessary.
The theory is discussed by means of presentations. Illustrative demos are used to clarify the concepts discussed. The theory is interchanged with experimenting with the demos yourself. Course times are from 9.30 to 16.30.
After successful completion of the course the participants receive an official NoSQL Data Access certificate.
Module 1 : NoSQL Intro |
Module 2 : Column Oriented Stores |
Module 3 : Key Value Stores |
|
Defining NoSQL Reasons for NoSQL Big Data Relational Limitations Denormalizing Tables Dropping Constraints Transactional Guarantees Flexible Indexing MapReduce Algorithm No Single Product Query Languages Scalability |
Google Bigtable Column Storage Handling nulls Row Keys Ordering Column Families Fault Tolerance Distributed File System Versioning Properties HBase Hypertable Cloudata |
Key Sets Hashmaps Associative Arrays Unique Combinations Easy Lookup Berkeley DB Memory Cache In Memory Snapshot Memcached API Cache Expiration EHCache Redis and Cassandra |
Module 4 : Document Databases |
Module 5 : Graph Stores |
|
|
What are Documents? Semi Structured Data Data Formats XML, JSON, BSON and YAML Schema Adherence Record Differences Looseley Definition HTTP Protocol RESTFull Access Cross Language Access Apache Thrift Projections MongoDB and CouchDB |
Graph Modeling Property Graph Model Node Labels Relationship Types Neo4J Cypher Queries Path Finding Queries Query Parameters Graph Global Operations Design for Query Ability In Graph Indexes Granulate Nodes FLockDB |
