-
Learning by doing
-
Trainers with practical experience
-
Classroom training
-
Detailed course material
-
Clear content description
-
Tailormade content possible
-
Training that proceeds
-
Small groups
In the course Microservices with Spring Boot, participants learn how to use Spring Boot to quickly and efficiently develop microservices in the form of fat jars with an embedded server. These Spring Boot microservices can be deployed independently and started as processes.
The course starts with an overview of the how and why of microservices. Microservices were developed in response to problems with monolithic applications that have proven to be difficult to maintain and expand over time. With a Microservices Architecture, the total functionality is realized by cooperating microservices, each of which falls under the responsibility of a team.
The Spring Boot Framework is ideally suited for the development of microservices because with Spring Boot applications all dependencies are included in a jar. Also Spring Boot applications can easily be provided with an embedded server so that the microservices can communicate via HTTP.
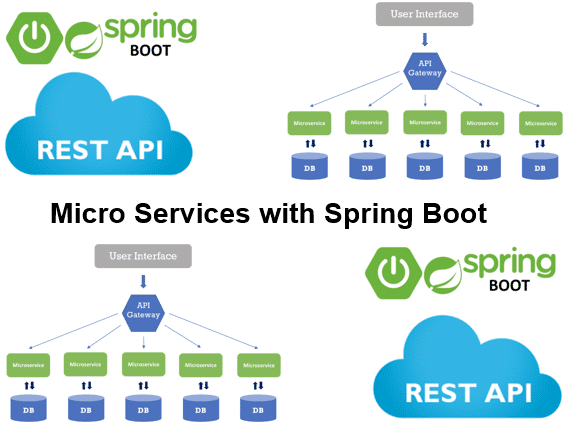
In the course Microservices with Spring Boot, various inter-process communication mechanisms between the microservices are discussed, such as synchronous communication via a REST API and asynchronous communication via messaging. Communication via a binary protocol is also on the agenda.
Attention is also paid to the ways in which microservices find each other. Both client side discovery and server side discovery are discussed. The use of tooling and utilities such as Netflix Eureka and Apache Zookeeper is covered as well.
Handling Data in Spring Boot Microservices is also part of the course program. Microservices often have their own database and it is explained how in that case transactions can be handled that concern different microservices. An event driven architecture as well as local and compensating transactions are treated.
Various options are available for the deployment of Microservices, including virtual machines and containers. In particular the deployment of the Spring Boot Microservices in docker containers is treated. Container orchestration with Kubernetes is also on the agenda. Finally the strategies to transform a monolithic architecture into a microservices architecture are discussed.
The course Microservices with Spring Boot is intended for experienced Spring Java Developers who want to use Spring Boot to develop Microservices.
Experience with programming in Java and Spring is required to participate in this course. Basic knowledge of a Microservice Architecture is beneficial understanding.
The concepts are discussed on the basis of presentation slides and demos. The theory is interchanged with exercises. Course times are from 9:30 to 16.30.
After successful completion of the course the participants receive an official certificate Microservices with Spring Boot.
Module 1 : Microservices Intro |
Module 2 : Using an API Gateway |
Module 3 : Spring Boot |
|
What are MicroServices? Components and Services Loose coupling Passing Messages Design Characteristics Simplicity and Transparency Reproduceability Asynchronous calls Mocking Components Testing Components Debugging Components |
REST Web Services GET, POST, PUT, DELETE @RestController Default Content Types @ResponseStatus and HttpStatus Working with XML and JSON Multiple Representations Filtering with @JsonView REST Clients RestTemplate Sending HTTP Requests |
Convention over Configuration No XML Spring Boot CLI Building and Deploying Using Templates Gathering Metrics Using Java With start.spring.io Spring Boot Starters Building as a Runnable JAR Data Access with Spring Data Property Support |
Module 4 : Interprocess Communication |
Module 5 : Discovery Patterns |
Module 6 : Data Management |
| Interaction Styles Request/response Notification Publish/Subscribe Synchronous vs Asynchronous Messaging Rest Synchronous IPC Apache Thrift Message Formats |
Client Side Discovery Load Balancing Service Registry Netflix Eureka Example Client Side Drawbacks Server Side Discovery Request Routing Kubernetes Apache Zookeeper Self Registration Pattern |
Distributed Data Problems ACID Transactions Distributed Transactions Polyglot Persistence Event Driven Architecture Eventual Consistency Achieving Atomicity Local Transactions Compensating Transactions Mining Transaction logs |
Module 7 : Deployment Strategy |
Module 8 : Refactoring to Microservices |
|
| Multiple Services Pattern Process or Process Group Multiple Service Instances per Host No isolation drawback Service Instance Per Host Service Instance per VM Service Instance per Container Docker and Kubernetes Serverless Deployment |
Monolitic Applications Application Modernization Big Bang Rewrite Glue code Split Frontend and Backend Extract Services Prioritizing Extract Modules Shrinking the Monolith |
