-
Learning by doing
-
Trainers with practical experience
-
Classroom training
-
Detailed course material
-
Clear content description
-
Tailormade content possible
-
Training that proceeds
-
Small groups
The course Jakarta EE Web Development covers how servlets and JSPs are constructed and used in Jakarta EE Web Applications.
First the main methods of servlets are on the agenda, like the ones used in servlet initialization, reading HTTP request data and writing HTTP response data.
The different scopes of Web Applications such as session scope and application scope are explained. Next the basic syntax of JSP's scriptlets, expressions and declarations are covered and the different JSP page directives are treated.
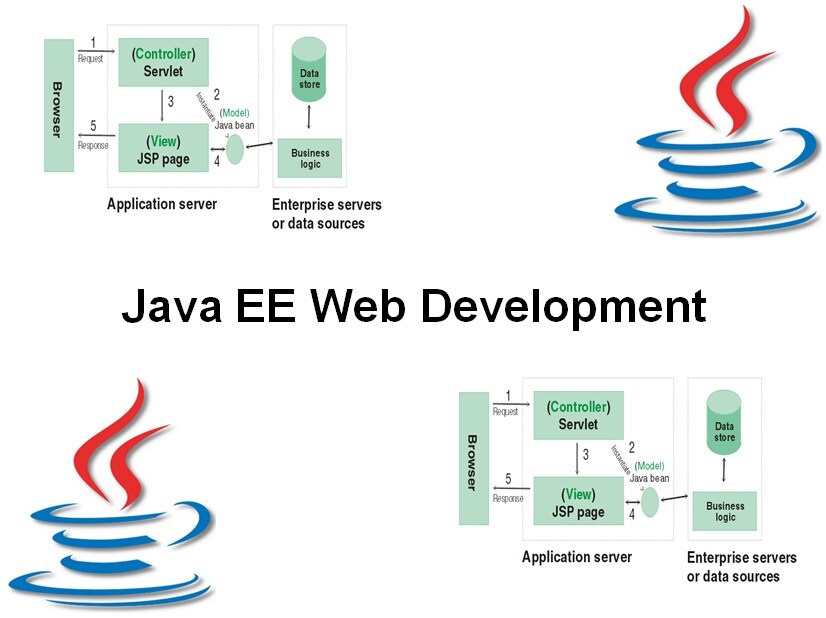
A central element in the course is the MVC design pattern for Java Web Applications where servlets act as controller for program logic and JSP's as view for output data. In discussing this pattern, the RequestDispatcher interface is treated as well as the ways attributes can be stored and retrieved in different scopes.
Ample attention is paid to techniques to separate Java code from the JSP view. In particular the use of Java beans and custom tags for this purpose is discussed.
Also the role of deployment descriptors is part of the subject matter and security in Web applications, filters and the event framework are addressed.
The course Jakarta EE Web Development is intended for developers who want to build Java Web applications with Jakarta EE components like Servlets, JSP's custom tags, filter and event listeners.
To participate in this course experience with Java programming and object orientation is required.
The theory is treated on the basis of presentation slides and is interspersed with exercises. Demos are used to clarify the theory. All topics asked at the Java Web Component Developer Exam are discussed. The course material is in English.
Participants receive an official certificate Jakarta EE Web Development after successful completion of the course.
Module 1 : Introduction |
Module 2 : Servlets |
Module 3 : Scopes and Sessions |
|
Jakarta EE Standard Jakarta EE Servers What is a Servlet? Possible Servlet Tasks What is a Java Server Page(JSP)? Problems with Servlets and JSP Classic MVC Pattern Model 2 Architecture Structure of a Web Application Registering a Web Application Defining Custom URL's WAR Files Handling Relative URL's |
Servlet Interface Reading Initialization Parameters Concurrent Access ServletContext Interface Destroying Servlets HTTP Requests and Responses HttpServlets service, doGet and doPost Reading Form Data HTTP Request Headers Populating the Response HTTP Status Codes HTTP Response Headers |
Sharing Data with Scope Objects ServletContext Application Scope Request Scope Page Scope Session Scope Session Tracking Mechanisms Sending and Reading Cookies Session Tracking with Cookies URL Rewriting Hidden Form Fields HttpSession methods Session tracking API |
Module 4 : JSP's |
Module 5 : JSP Directives |
Module 6 : JSP Standard Actions |
| The Need for JSP Types of Scripting Elements Benefits of JSP Translation and Request Time Setting up your environment Expressions Predefined Variables Scriptlets Declarations jspInit and jspDestroy |
What are JSP directives JSP page Directive import Attribute contenttype Attribute session Attribute buffer and autoflush Attributes extends Attribute errorPage and isErrorPage include Directive taglib Directive |
jsp:include jsp:plugin, jsp:param and jsp:params What are Beans? Basic use of Beans in JSP Accessing Bean Properties Setting Bean Properties Explicitly Association with Input Parameters Sharing Beans Values of Scope Attribute Conditional Bean Operations |
Module 7 : MVC Architecture |
Module 8 : Expression Language |
Module 9 : Custom Tags |
| Why combine Servlets and JSP? MVC Approach Implementing MVC Dispatching requests Storing Data in Servlet Request Storing data in Session Storing data in ServletContext Forwarding Requests Including Requests |
Advantages Expression Language Activating Expression Language Invoking the EL Common EL Problem Referencing Scoped Variables Accessing Bean Properties Nested Beans Using EL Operators Conditional Evaluation |
What are Tag Libraries? Custom Tag Features Simple Tag Handler Simple Tag Library Descriptor Accessing Custom Tags from JSP Attributes and Body Content JSP-based Tags Tags manipulating Body Complex Objects for Attributes |
Module 10 : Security |
Module 11 : Filters |
Module 12: Event Listeners |
| Major Security Concerns Declarative Security Programmatic Security Form-based Authentication Deployment Descriptor settings BASIC Authentication Combining Security Mechanisms Pure Programmatic Security Programmatic Security with SSL |
What are Filters? Filter Interface Creating Filters doFilter method Servlet Filter Related Classes Filters in a Chain Filter Mapping Accessing the Servlet Context Filter Initialization Parameters |
Life-Cycle Events Framework Available Listeners Implementation Strategy Reason for listeners ServletContext Listeners ServletContextAttributeListeners HttpSession Listeners Session Creation Events SessionAttribute Listeners |
